Day 87: Implementing Rate Limiting and Quota Management for Distributed Log APIs
Module 4: Building a Complete Distributed Log Platform | Week 13: API and Service Layer
Agenda
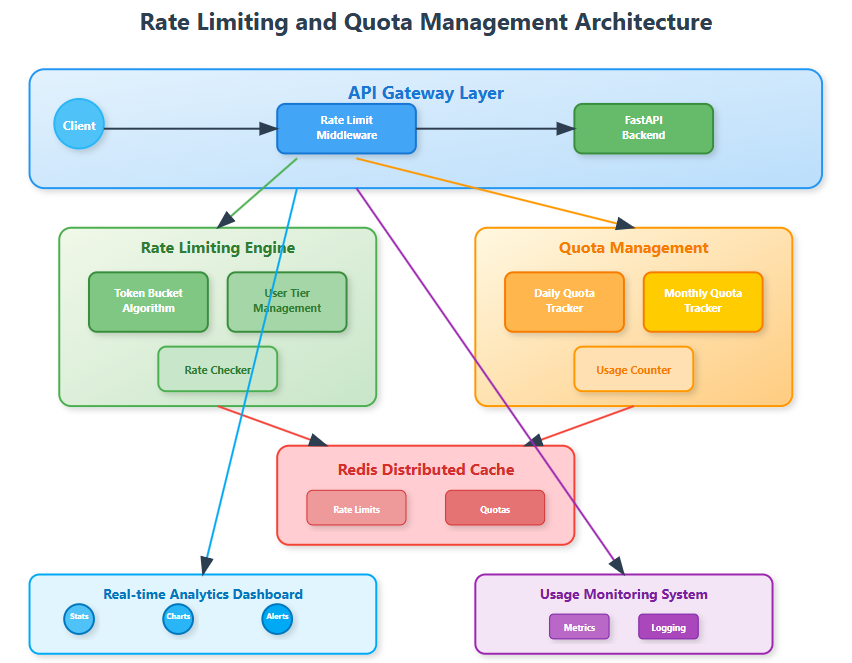
Today you're building the protective shield around your distributed log processing API - a sophisticated rate limiting and quota management system that prevents abuse and ensures fair resource distribution.
Key Components We'll Implement:
Token bucket rate limiter with configurable limits
Sliding window quota tracking system
Real-time usage monitoring dashboard
Distributed enforcement across multiple API nodes
Integration with existing GraphQL endpoint from Day 86
The Protection Problem
Imagine Spotify's logging API without rate limits - a single misbehaving client could flood their system with millions of log ingestion requests, degrading service for all users. Rate limiting acts like intelligent traffic control, allowing legitimate usage while blocking malicious or excessive requests.
Twitter's API famously uses rate limiting to prevent abuse while enabling developers to build applications. Similarly, your log processing API needs protection mechanisms that distinguish between legitimate high-volume usage and potential attacks.
Core Concepts
Rate Limiting Algorithms
Token Bucket Algorithm: Each user gets a bucket with tokens. Requests consume tokens, and buckets refill at a steady rate. This allows burst traffic while maintaining long-term limits.
Sliding Window Counter: Tracks request counts over rolling time windows. More memory-intensive but provides smoother rate enforcement compared to fixed windows.
Distributed Enforcement: Rate limits must work across multiple API server instances, requiring shared state management through Redis or similar systems.
Quota Management
Unlike rate limits (requests per time period), quotas track cumulative usage over longer periods - daily log ingestion limits, monthly API calls, or storage quotas. These require persistent tracking and periodic resets.